What is Edge Computing?
Understanding the Future of Decentralized Data Processing
As our world becomes increasingly connected—with smart homes, autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and AI applications—there’s an overwhelming volume of data being generated every second. Traditionally, this data is sent to centralized cloud servers for processing and analysis. But what happens when this approach becomes too slow, expensive, or insecure?
Enter Edge Computing—a transformative solution that brings data processing closer to the source of data generation. In this blog, we’ll explore what edge computing is, how it works, why it matters, and where it’s being used today.
What is Edge Computing?
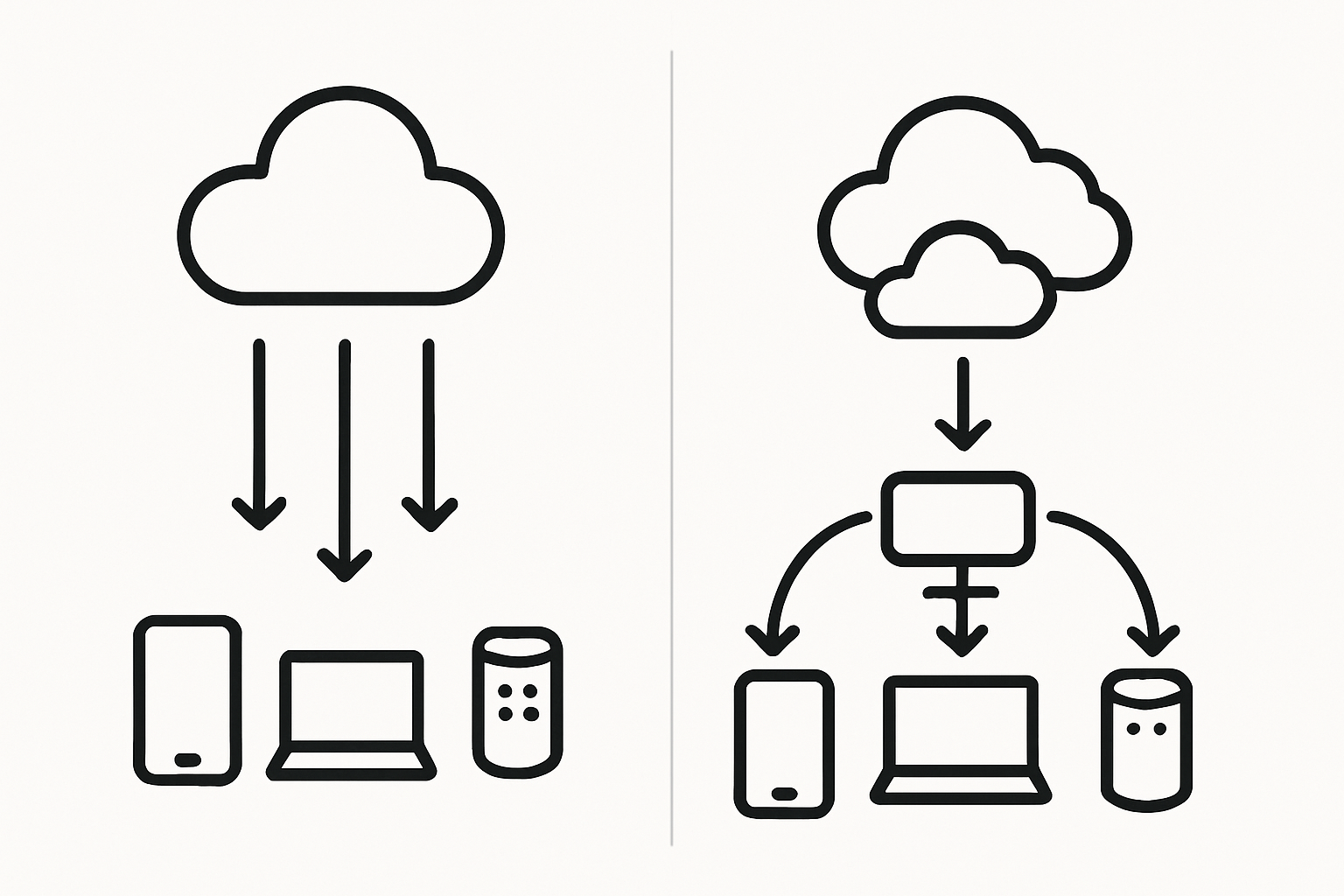
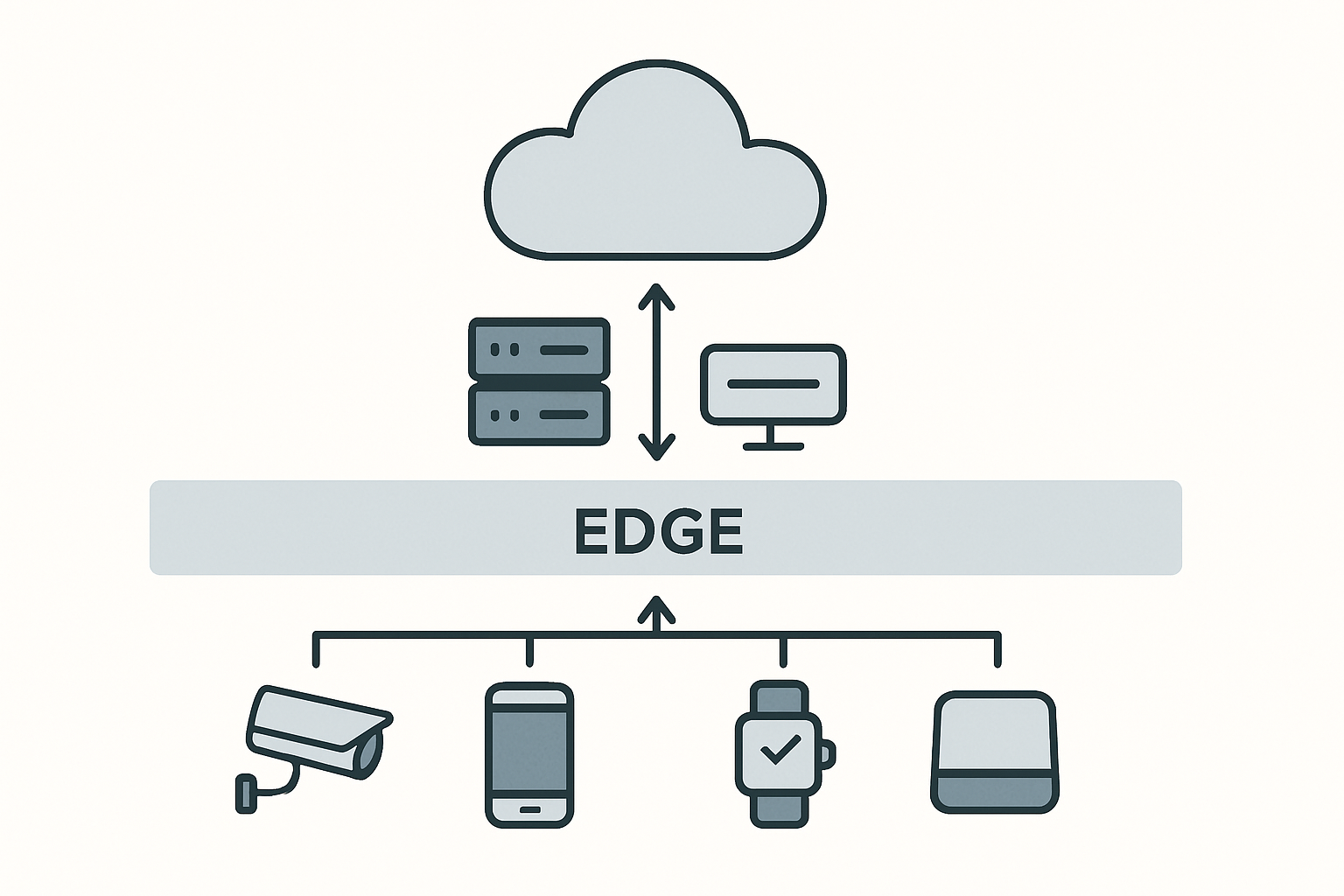
Edge computing is a decentralized computing model that enables data processing at or near the physical location where data is created, rather than relying entirely on centralized data centers.
Instead of sending all raw data to the cloud, edge computing devices analyze and process it locally—or on “the edge” of the network. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and enhances real-time decision-making.
In Simple Terms:
Imagine a smart camera that detects motion. Instead of uploading every second of video to the cloud, it processes footage locally and only sends relevant clips—like when it detects a person—to the cloud for storage.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing involves multiple layers and components:
- Edge Devices
- Sensors, smartphones, industrial robots, smart cameras, etc.
- Generate and sometimes process data locally.
- Edge Nodes or Gateways
- Intermediate hardware (e.g., routers or micro data centers) that aggregate and analyze data from edge devices.
- Can run lightweight machine learning models or trigger actions without cloud input.
- Cloud or Central Servers (Optional)
- Used for heavier data processing, long-term storage, or model training.
Key Technologies Involved:
-
AI/ML on the edge
-
5G networks
-
Containerization (e.g., Docker)
-
Real-time analytics platforms
Benefits of Edge Computing
✅ Low Latency
Processes data in milliseconds—essential for real-time applications like autonomous cars, AR/VR, or industrial automation.
✅ Reduced Bandwidth Usage
Only relevant data is sent to the cloud, reducing data transfer costs and avoiding network congestion.
✅ Enhanced Privacy & Security
Sensitive data (like medical records or camera footage) can be processed locally without ever leaving the device.
✅ Greater Reliability
Devices can still operate with limited or no internet connectivity—ideal for remote locations or mission-critical tasks.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Factories use edge computing to monitor machinery, predict maintenance needs, and avoid downtime.
Healthcare
Medical devices analyze patient data in real-time—vital for remote patient monitoring or smart diagnostic tools.
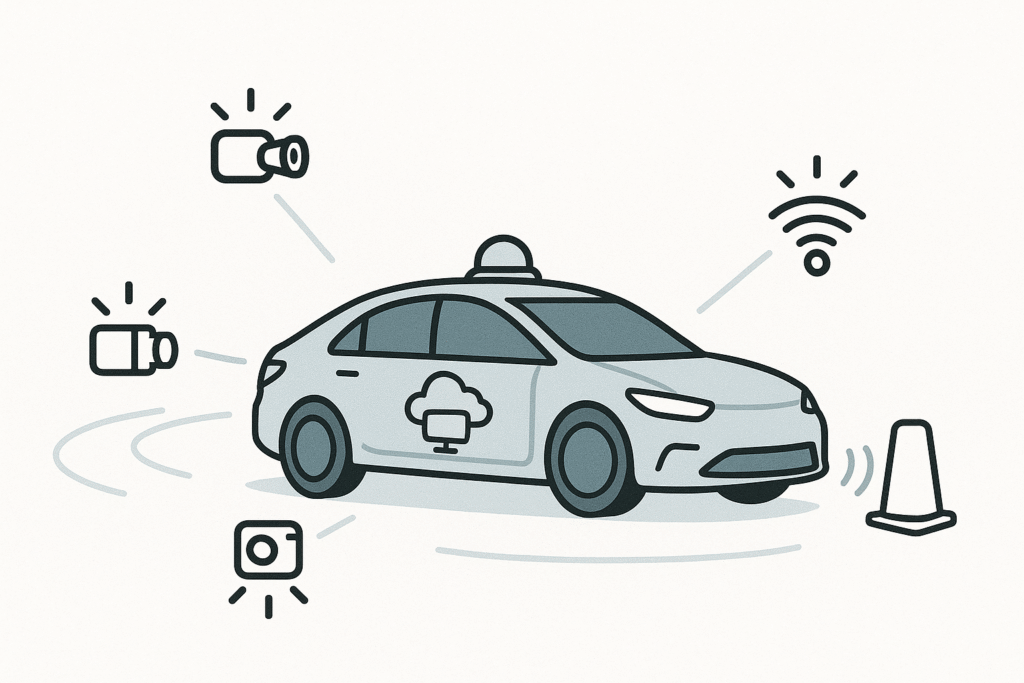
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing helps process sensor data instantly for navigation, obstacle avoidance, and safety systems.
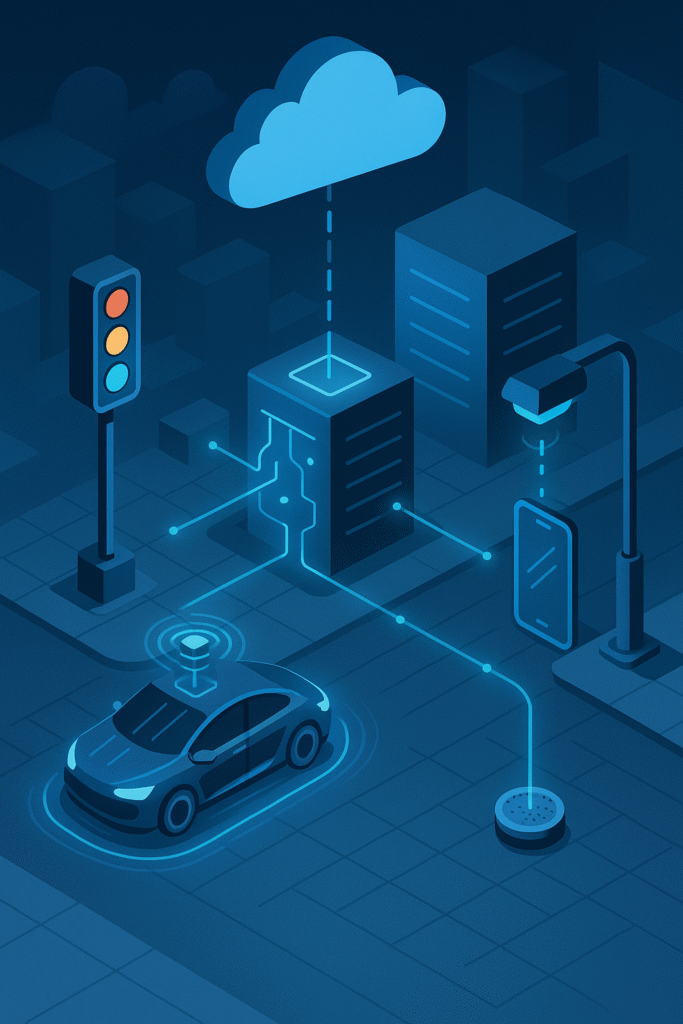
Smart Cities
Traffic lights, surveillance systems, and energy grids rely on edge computing for efficiency and responsiveness.
Retail
Smart shelves and checkout-free stores (like Amazon Go) use edge devices for object detection and inventory tracking.
Edge vs. Cloud: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Higher (data travels far) | Ultra-low (data stays local) |
| Bandwidth Use | High | Lower |
| Reliability | Internet-dependent | Works offline |
| Use Case | Centralized analytics | Real-time, localized tasks |
In reality, edge and cloud are complementary. Edge computing handles time-sensitive tasks locally, while the cloud manages long-term data storage and analysis.
Future of Edge Computing
With the rise of:
- 5G networks
- AI-powered IoT
- Connected devices in every industry
…edge computing will play a crucial role in creating faster, smarter, and more responsive systems.
According to industry forecasts, the global edge computing market is expected to surpass $100 billion by 2030.
Conclusion
Edge computing isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a paradigm shift. By pushing computation closer to the source of data, edge computing unlocks new levels of speed, security, and efficiency.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, business leader, or developer, understanding edge computing is essential for navigating the next wave of innovation.